Today, September 4, is National Wildlife Day. I had never heard of it before, but a Nature Conservancy newsletter that arrived today happened to mention it. It’s been around since 2006.
According to the National Wildlife Day website, the day is brought to us by the Animal Miracle Network. And if you have never heard of that either, that’s because it’s a pet rescue organization. (I could not find any media on any of this that was not a rehash of a press release, or just a press release.)
Again, according to the website, animal advocate Colleen Paige, founder of the Animal Miracle Network, created the day in 2006 to honor Animal Planet star Steve Irwin and the zoos and animal sanctuaries that preserve endangered wildlife and educate the public about their plight.
The website says that National Wildlife Day aims to focus attention on the endangered animals that need to be preserved and rescued. (I would just quote the sentence from the website, but the website denies that use without prior permission, even though it would be “fair use,” under copyright law.) So you can kind of see the train of thought here: rescuing cats and dogs, rescuing wildlife.
Don’t get me wrong, I love zoos, respect their work, and honor the way they allow people to connect with animals. But if this is the point, how about calling it National Zoo Day?
A day devoted to the idea that keeping endangered wildlife captive is a way to protect it is worrisome. This, of course, is just one tool, and a last-ditch one, in a very large toolbox. It feels like the guiding spirit here is the pet-ification of wildlife (my clues are the photos of the founder hugging a wolf and kissing a bear), although it may be simply retro, or even deliberately choosing to focus on this tiny piece of the conservation puzzle even though it’s not the dominant technique.
National Wildlife Day is doing its best to control the message that goes out under its name, which is really too bad. Who can argue against a day to recognize wildlife, except, as is the case, if it focuses on one tiny aspect of wildlife — endangered species — and just one of many techniques for helping those species. As far as I know, it’s not an official day, of the sort recognized by Congress or a state legislature.
In fact, National Wildlife Day didn’t make the “Days of the Year” website (which is just a random website, and is also not official), but the much more mainstream Endangered Species Day (May 16, 2014 — mark your calendars) did.


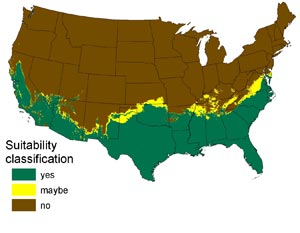 In 2008 the US Geological Survey published a report that said that the entire southern third of the United States could provide habitat for the invasive Burmese python that has been roiling the Florida Everglades ecoystem.
In 2008 the US Geological Survey published a report that said that the entire southern third of the United States could provide habitat for the invasive Burmese python that has been roiling the Florida Everglades ecoystem.