|
| Credit: KDFWR |
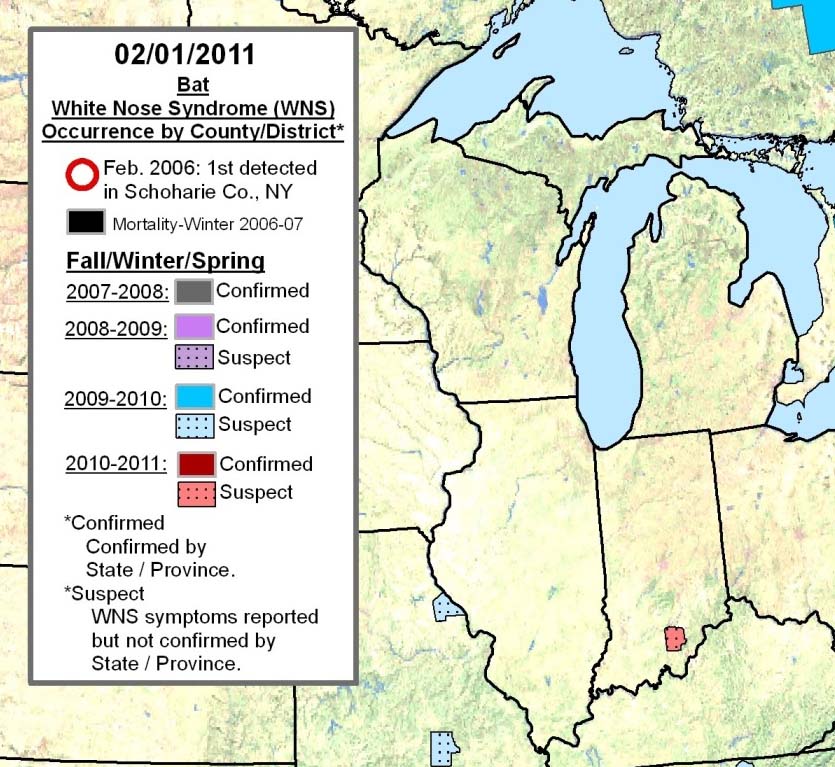
A little brown bat in Trigg County, Kentucky had white nose syndrome. The Southeastern Cooperative Wildlife Disease Study (SCWDS) in Athens, Georgia confirmed the diagnosis. The bat was found in a privately owned cave in southwest Kentucky, about 30 miles southeast of Paducah, the Kentucky Department of Fish and Wildlife Resources reports.
No other infected sites were found in a search of caves within a 16 mile radius of the cave. However, 60 “highly suspect” little brown and tri-colored bats were euthanized. Killing the bats, which were not expected to survive, were among the measures the state took to prevent the spread of white nose syndrome beyond this cave, which is a haven for about 2,000 hibernating bats.
“This is likely the most significant disease threat to wildlife Kentucky has ever seen”, said Kentucky Fish and Wildlife Commissioner, Dr. Jonathan Gassett in a press release. “It would be professionally irresponsible to take no action to stop or slow this disease.”
In 2009 Kentucky created a white nose syndrome response plan that included actions to take both before and after the syndrome arrived in the state. Indeed, what makes the Kentucky case unusual is that the state is taking steps to slow or stop the disease and is telling the public about them. We’ll stay tuned to see what happens.
For more information, read the Kentucky Fish and Wildlife Resources press release. Or read the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service press release, which appears to be identical. Or, read this report from the Louisville Courier-Journal. A few other local news outlets also have the story.