 In a recent study on the origins of the fungus that causes white nose syndrome in bats, the bats in the study were monitored with infrared cameras. This allowed the researchers to see when the bats were rousing (they need to warm up first).
In a recent study on the origins of the fungus that causes white nose syndrome in bats, the bats in the study were monitored with infrared cameras. This allowed the researchers to see when the bats were rousing (they need to warm up first).
Read a mention of the infrared monitoring in this Associated Press story on the Yahoo News site.
You can also find the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences paper here, but you need a subscription or to pay a fee to read the whole paper.
A more common use for infrared imaging has been for wildlife surveys. For example, Tennessee Wildlife Resources Agency has used thermal imaging to survey the ratio of bucks to does and does to fawns for deer management. But this technology can do more.
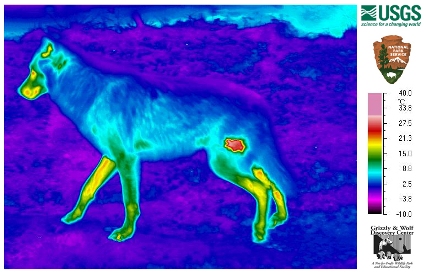
Scientists are using infrared thermal imaging cameras to detect sarcoptic mange in Yellowstone wolves. The patches of bare skin caused this form of scabies stress the animal because the calories used up to compensate for the heat loss can doom the animal.
Read an article on an early stage of the study in the Billings Gazette.
Read information from the US Geological Survey, here.
And a tip of the hat to Wired Magazine, which dedicated a full page to the story in its May 2012 issue. (Sorry, no direct link because the May issue wasn’t online when this was posted.)
While the Billings Gazette article describes the scientists renting a $40,000 camera, in the Wired Magazine update, $4,000-$5,000 per camera is the price mentioned. There seem to be a lot of possibilities for using infrared thermal imaging in wildlife management that go beyond surveys.
Photo: Thermal image of a wolf with a small bald spot on its rear leg, from the initial test of concept. Courtesy of the US Geological Survey.

Pingback: 2012 Year in Review | State Wildlife Research News