Hunters have been turning up elk with deformed hooves in southwest Washington for nearly 10 years. In the past six years or so, the numbers of those reports have increased. The first reports of elk hoof deformities in Oregon were reported this summer,The Oregonian reported.
This week the Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife announced an online reporting system to make it easier for hunters to report elk with deformed hooves, so that the department can track the deformities in northwestern Oregon. The online form also requests that the hunter take pictures of the hooves, wrap them in plastic bags and store them in a cool place for further examination later.
For many years, the cause of the elk hoof deformities was a mystery. Today the Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife believes that treponemes, spiral-shaped bacteria, likely cause the disease, according to the article in The Oregonian. Livestock have a similar disease, the article says.
Read the Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife press release, here.
Read the August article from The Oregonian, here.

 Why are mule deer declining in Western states? So far, that’s a mystery. The
Why are mule deer declining in Western states? So far, that’s a mystery. The  In February, the Nebraska Game and Parks Commission collared 11 elk for a study in north-central Nebraska. There are a few more details in this
In February, the Nebraska Game and Parks Commission collared 11 elk for a study in north-central Nebraska. There are a few more details in this Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) was first detected in Pennsylvania in 2012 at a captive facility in Adams County. Subsequently, three free-ranging deer harvested by hunters during the 2012 season tested positive for CWD. Now,
Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) was first detected in Pennsylvania in 2012 at a captive facility in Adams County. Subsequently, three free-ranging deer harvested by hunters during the 2012 season tested positive for CWD. Now, Wyoming Game and Fish Department personnel, researchers with the Wyoming Cooperative Fish and Wildlife Research Unit at the University of Wyoming, personnel from the Bureau of Land Management and US Forest Service, and many volunteers are trapping mule deer for two research projects in southwest Wyoming, a
Wyoming Game and Fish Department personnel, researchers with the Wyoming Cooperative Fish and Wildlife Research Unit at the University of Wyoming, personnel from the Bureau of Land Management and US Forest Service, and many volunteers are trapping mule deer for two research projects in southwest Wyoming, a 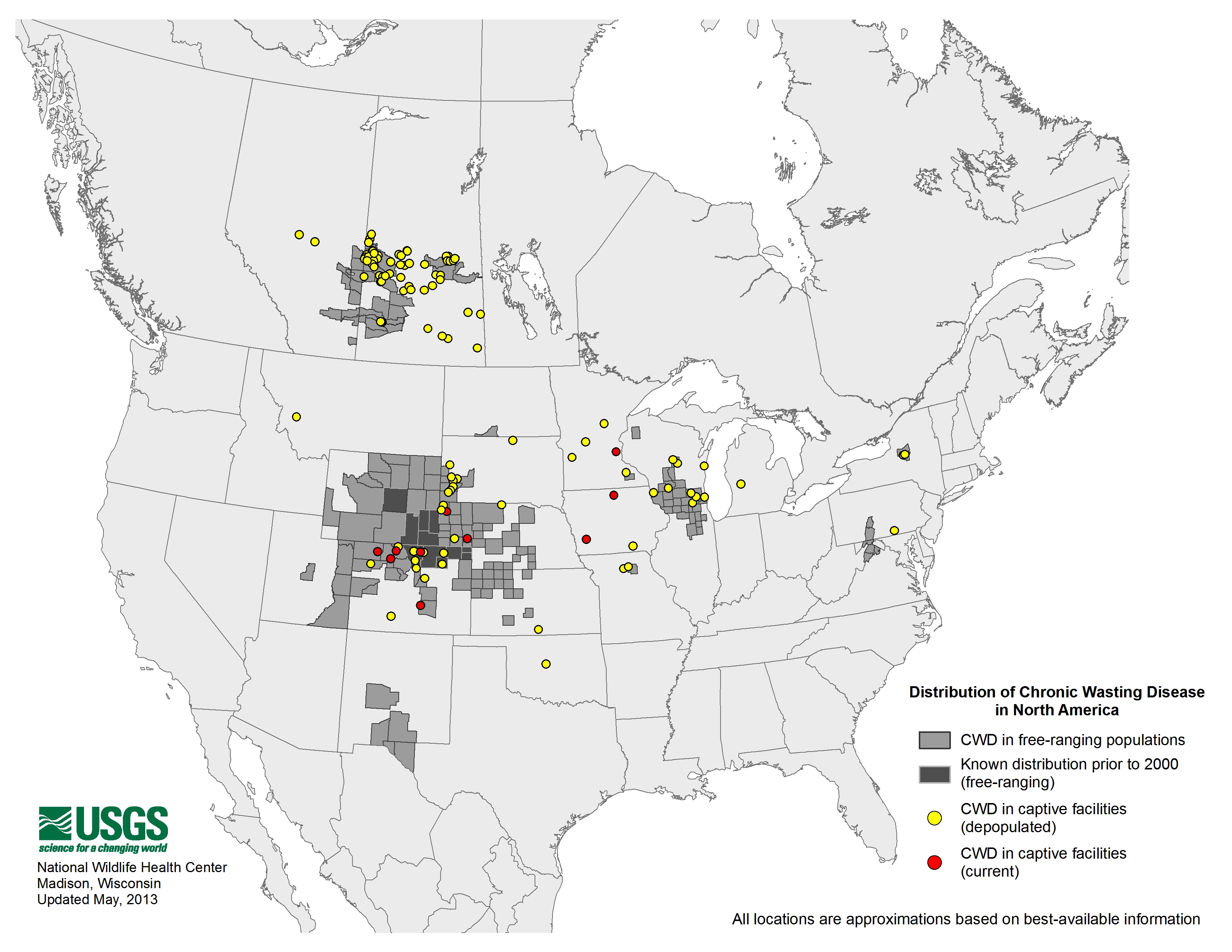 Plants, including crop plants such as alfalfa and tomatoes, may serve as a reservoir for the prions, or misfolded proteins, that cause chronic wasting disease in deer (as well as other prion diseases such as scrapie in sheep, and mad cow disease), reports
Plants, including crop plants such as alfalfa and tomatoes, may serve as a reservoir for the prions, or misfolded proteins, that cause chronic wasting disease in deer (as well as other prion diseases such as scrapie in sheep, and mad cow disease), reports 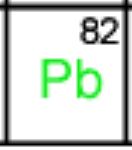 Two stories today focus on two different states’ efforts to get lead out of the environment.
Two stories today focus on two different states’ efforts to get lead out of the environment.
